Mastectomy
Whole breast reconstruction is a surgical procedure performed to recreate the breast after a mastectomy (removal of the breast, often due to cancer or other medical conditions).

The goal is to restore the shape, appearance, and symmetry of the breast while addressing the patient’s physical and emotional needs.
Types of Breast Reconstruction
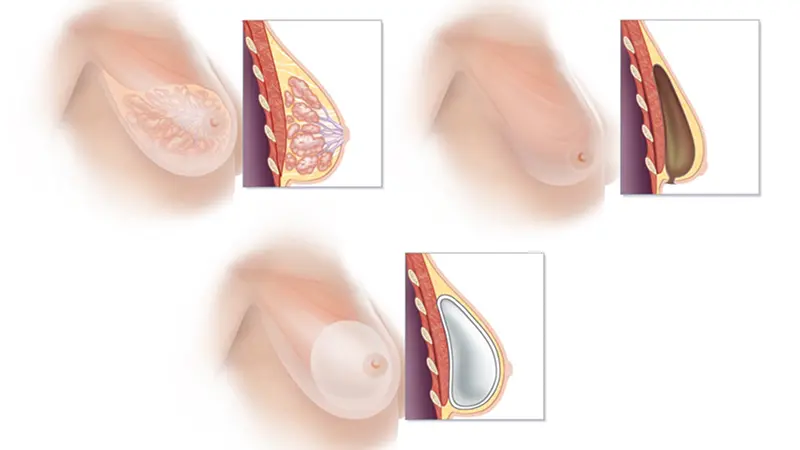
Implant-Based Reconstruction
Description
Utilizes silicone or saline implants to rebuild the breast.
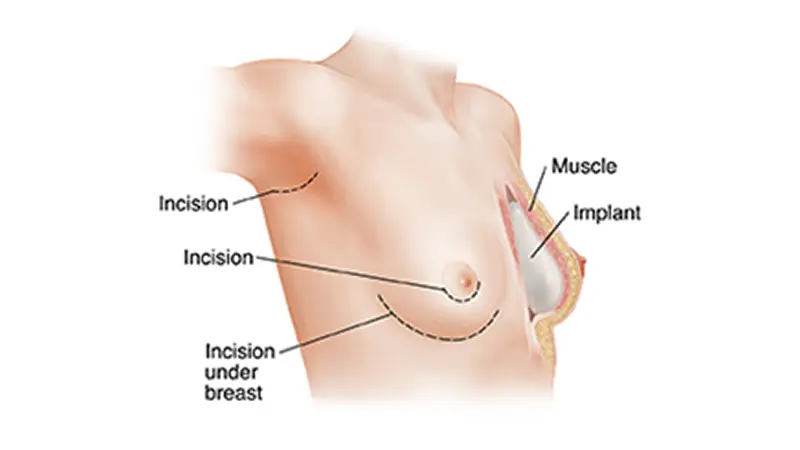
Procedure
- Immediate Reconstruction: Performed during the same surgery as the mastectomy.
- Two-Stage Reconstruction: Involves placing a tissue expander during mastectomy, which is gradually filled with saline over weeks. Once the chest tissue stretches adequately, the expander is replaced with a permanent implant.
Autologous (Flap) Reconstruction
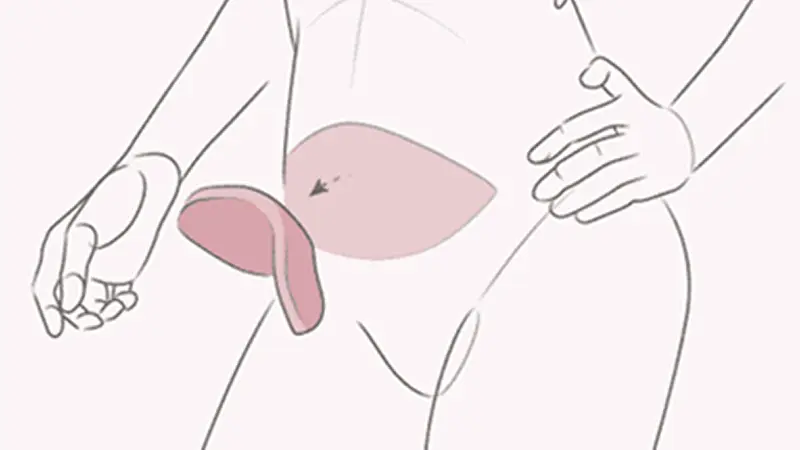
Description
Uses the patient’s own tissue from another part of the body, such as the abdomen, back, thighs, or buttocks.
Common Flap Types
- DIEP Flap (Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator) : Tissue is taken from the abdomen without removing the underlying muscle.
- TRAM Flap (Transverse Rectus Abdominis Myocutaneous) : Involves skin, fat, and muscle from the abdomen.
- Latissimus Dorsi Flap : Tissue is taken from the upper back.
- SGAP/IGAP (Superior/Inferior Gluteal Artery Perforator) : Tissue from the buttocks is used.
Hybrid Reconstruction
Description
Combines implants and autologous tissue. Fat grafting may also be used to refine the reconstructed breast.
Nipple and Areola Reconstruction
Description
After the breast mound is reconstructed, the nipple and areola can be recreated using techniques such as tattooing, skin grafting, or 3D tattooing for a natural appearance.
Timing of Reconstruction
- Immediate Reconstruction : Performed during the mastectomy. Offers psychological benefits and fewer surgeries.
- Delayed Reconstruction : Performed after the mastectomy and/or additional treatments like radiation or chemotherapy. Allows time for recovery and decision-making.
- Delayed-Immediate Reconstruction : A tissue expander is placed during mastectomy, allowing reconstruction to be completed after additional treatments if needed.
Recovery Timeline
Immediate Post-Surgery (1-2 weeks)
- Pain, swelling, and bruising are common. Pain is managed with medication.
- Drains may be placed to prevent fluid buildup.
- Limited movement and activity.
Weeks 3-6
- Swelling reduces, and light activities resume.
- Follow-up visits to monitor healing.
Months 3-12
- Scars begin to fade, and final results become apparent.
- Additional procedures (e.g., nipple reconstruction or fat grafting) may be scheduled.
Psychological Impact
Breast reconstruction can improve body image and self-confidence, helping patients feel more comfortable in their appearance after a mastectomy. Emotional support, including counseling or support groups, may enhance the overall experience.




